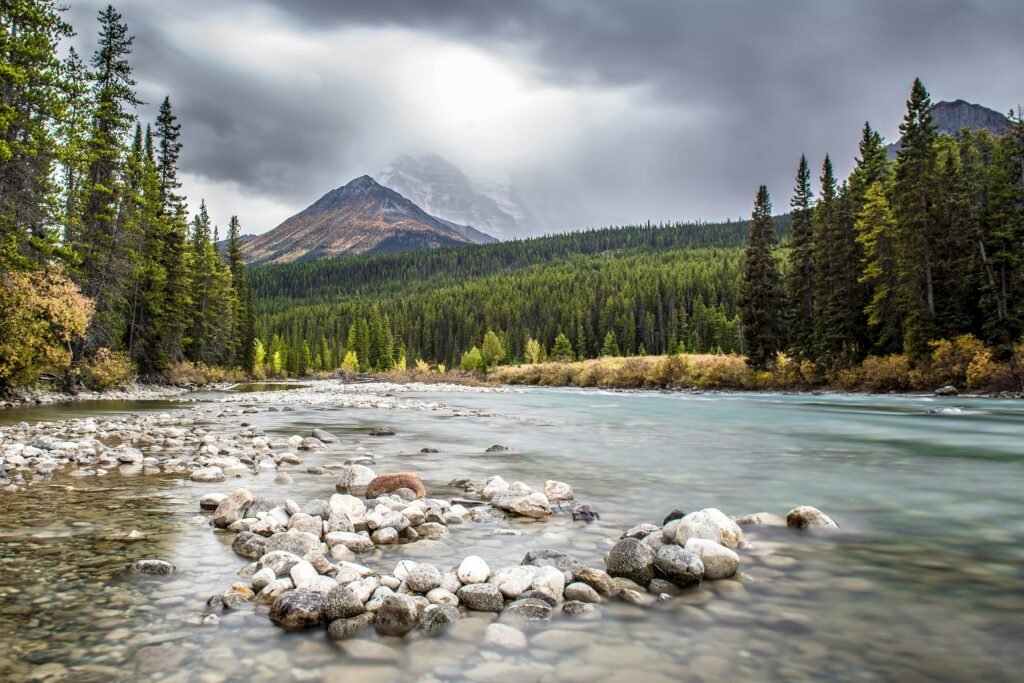
Imagine powering your cabin, home, or business entirely from the sun — no hydro bills, no grid connection, and complete control over your energy. That’s the promise of an off-grid solar system.
In 2025, off-grid technology has become more affordable, efficient, and practical than ever before. Whether you’re living in a remote area or simply want energy independence, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know about off-grid solar in Canada — from components and sizing to costs and real-world performance.
What Is an Off-Grid Solar System?
An off-grid solar system is a stand-alone power setup that operates independently from the electrical grid. It generates, stores, and delivers electricity using solar panels, battery storage, and inverters — with no reliance on a public utility.
Off-grid systems are ideal for:
-
Remote properties without grid access
-
Cabins and cottages
-
RVs, boats, and mobile setups
-
Homeowners seeking energy independence or backup power
Unlike grid-tied systems, an off-grid setup must produce 100% of your electricity needs, so proper design and sizing are critical.
Main Components of an Off-Grid Solar System
A reliable off-grid solar setup includes five key components:
1. Solar Panels
Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
Most systems use monocrystalline panels for higher efficiency in limited roof space — a must for Canadian winters and short daylight hours.
Tip: Look for panels rated for cold temperatures and snow loads — like those certified under CSA or IEC 61215 standards.
2. Charge Controller
A charge controller regulates the voltage and current coming from the panels to prevent overcharging your batteries.
Modern MPPT controllers (Maximum Power Point Tracking) are 20–30% more efficient than older PWM models — especially in variable Canadian weather.
3. Battery Bank
Batteries store excess energy for use at night or during cloudy days. In 2025, lithium-iron phosphate (LiFePO₄) batteries have become the top choice for off-grid systems due to:
-
Longer lifespan (up to 15 years or more)
-
Deep discharge capacity
-
Maintenance-free operation
-
Better cold-weather performance than lead-acid
Popular battery options in Canada include Enphase IQ Batteries, Discover AES, and EG4 LiFePower4 systems.
4. Inverter
The inverter converts the stored DC power into usable AC electricity for your appliances and devices.
Pure sine-wave inverters are essential for modern electronics, and hybrid inverter-chargers (like Victron Multiplus or Growatt Off-Grid Series) allow seamless generator integration.
5. Backup Generator (Optional but Recommended)
For most Canadian off-grid setups, a backup generator (propane, diesel, or gas) provides peace of mind during extended cloudy periods.
It can automatically charge your batteries when solar production dips — keeping your lights and heat on even in deep winter.
How to Size Your Off-Grid Solar System
Sizing correctly is crucial to avoid running out of power or overspending.
Step 1: Determine Your Daily Energy Use
Add up the wattage of all appliances you plan to run and multiply by the hours of use.
Example:
|
Appliance |
Watts |
Hours/Day |
kWh/Day |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Fridge |
120 |
24 |
2.9 |
|
Lights (LED) |
60 |
5 |
0.3 |
|
Laptop & Router |
100 |
6 |
0.6 |
|
Water Pump |
400 |
1 |
0.4 |
|
Total |
4.2 kWh/day |
Step 2: Multiply by 1.3
To account for inverter loss, cloudy days, and temperature effects:
4.2 × 1.3 = ~5.5 kWh/day needed from solar.
Step 3: Size Panels and Batteries
-
Panels: Divide total energy by average daily sunlight (e.g., 5 kWh ÷ 4 sun hours ≈ 1.25 kW array).
-
Battery bank: For 2 days of backup using lithium batteries, you’d need about 11 kWh of storage capacity.
Costs of Off-Grid Solar Systems in 2025 (Canada)
|
System Size |
Application |
Approx. Cost (CAD) |
|---|---|---|
|
Small Cabin (1–2 kW) |
Lighting & essentials |
$5,000 – $8,000 |
|
Medium Home (4–6 kW) |
Basic off-grid living |
$12,000 – $20,000 |
|
Large Home (8–10 kW +) |
Full off-grid setup |
$25,000 – $40,000+ |
Note: Costs vary by location, component brand, and battery chemistry. Lithium systems cost more upfront but last twice as long as lead-acid.
Best Locations for Off-Grid Solar in Canada
Canada’s vast geography offers incredible opportunities for off-grid living. Some of the most popular provinces for solar self-sufficiency include:
-
British Columbia: Excellent for cabins and rural homes, especially interior BC.
-
Alberta: High sunlight hours year-round and strong off-grid community.
-
Ontario: Great incentives and off-grid cottage demand.
-
Nova Scotia / New Brunswick: Strong interest in hybrid solar-battery setups for coastal resilience.
Off-Grid vs. Hybrid Solar Systems
|
Feature |
Off-Grid |
Hybrid |
|---|---|---|
|
Grid Connection |
None |
Connected |
|
Energy Storage |
Required |
Optional |
|
Backup Generator |
Recommended |
Optional |
|
Utility Credits |
No |
Yes (via net-metering) |
|
Ideal Use |
Remote areas, total independence |
Homes seeking resilience + savings |
If your property already has grid access, a hybrid solar system might provide the best of both worlds: grid backup when needed, and full solar autonomy during outages.
Winter Performance Tips
Solar works even in winter — just less efficiently. To maximize output:
-
Use steeper tilt angles (40–50°) to capture low-angle sunlight and shed snow.
-
Keep panels clean after heavy snowfall.
-
Use lithium batteries (they handle cold far better than lead-acid).
-
Store electronics in insulated enclosures.
Advantages of Going Off-Grid
-
Total energy independence
-
Zero hydro bills
-
Sustainable and renewable power
-
Backup security during outages
-
Ideal for remote or rural properties
And perhaps most importantly — the peace of mind knowing your power is entirely your own.
The Future of Off-Grid Living in Canada
With technology improving every year, off-grid systems in 2025 are smarter, more modular, and easier to manage than ever before.
Smart monitoring, AI-driven battery management, and efficient solar hardware now make it realistic for almost any homeowner to live comfortably without a grid connection.